Understanding Strabismus (Crossed Eyes): Causes, Treatments, and Solutions
Strabismus (crossed eyes) isn’t just cosmetic—it disrupts depth perception and confidence. Learn causes, non-surgical fixes like vision therapy, and surgical solutions to realign eyes and restore 3D vision.
Correcting Eye Misalignment and Improving Sight
“Now I am able both to study and read for fun because my eyes don’t quit on me. My hand-eye coordination and my sports have also improved. More than anything, I’ve noticed that my right eye no longer turns in. People used to be able to tell when I was tired because my eye would always become lazy and turn in, but not anymore.”
Key Takeaways
-
Brain Coordination Issue: Strabismus (crossed eyes) stems from the brain’s inability to align the eyes, not just muscle weakness, often linked to genetics, poor vision, or underlying health conditions.
-
Beyond Cosmetic: Affects depth perception, risks amblyopia (lazy eye), and can lead to social challenges due to visible misalignment.
-
Non-Surgical Success: Vision therapy and corrective glasses improve eye-brain coordination, with studies showing 60–80% surgical success rates when combined with post-op therapy.
-
Surgical Precision: Procedures like muscle recession or resection realign eyes, though long-term stability often requires vision therapy to reinforce results.
-
Early Symptoms: Misaligned eyes, double vision, eye strain, head tilting, and difficulty judging distances signal potential strabismus.
-
Timely Diagnosis: Comprehensive exams (visual acuity tests, corneal light reflex) are critical to prevent vision loss, especially in children.
-
Age-Specific Care: Children benefit most from early intervention (glasses, patching), while adults focus on symptom management and functional improvement.
-
Holistic Approach: Combining surgery with vision therapy enhances depth perception and reduces recurrence, ensuring lasting alignment.
-
Proven Outcomes: Patient testimonials and clinical data highlight restored confidence, improved coordination, and 3D vision recovery.
What is Strabismus?
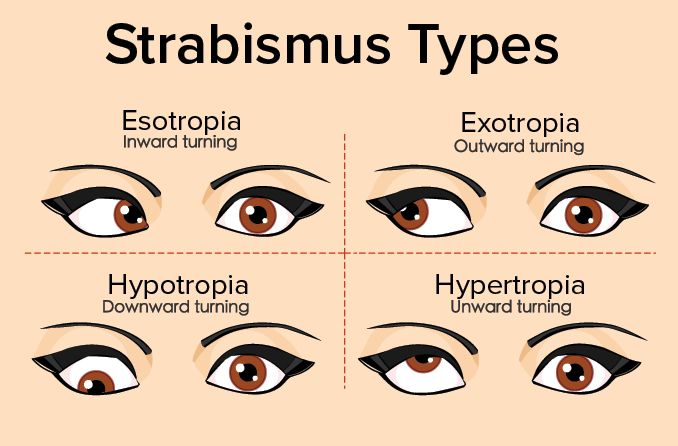
Strabismus, commonly known as crossed eyes, is a condition where the eyes do not properly align with each other when looking at an object. This misalignment can take various forms, including esotropia (an inward turn towards the nose) and exotropia (an outward turn towards the ear).
Not an Eye Muscle Problem
Strabismus is typically a brain problem, not an eye muscle problem. Each eye has six muscles on the outside of the eyeball. These muscles move and align the eyes. In about 5 cases out of a hundred, strabismus is caused by a damaged eye muscle–when the good eye is covered, the turned eye’s ability to move in all directions is limited. In most cases, however, the eye muscles are normal: when one eye is covered, the other eye moves freely in all directions. When both eyes are uncovered, an eye deviates because the BRAIN fails to coordinate the muscles to align the eyes.
The Cosmetic Problem
Strabismus causes a problem with appearance. Children on the playground make fun of the child whose eyes look different. Adults with strabismus are often embarrassed because others don’t know which eye to look at.
The Seeing Problem
Strabismus affects more than the way we look. It also affects the way we see. When eyes are straight, each eye sends its own picture to the brain. The brain combines these two pictures into a three dimensional image, thus creating “depth perception” or 3D Vision.
When an eye first crosses, the pictures from the two eyes no longer match and the world doubles and runs together. At this point, the person with the turned eye may run into things, knock over drinking glasses, etc. In time though, if the eye is allowed to continue crossing, the child usually learns to ignore or “suppress” the information from the deviated eye.
As a result, the child no longer suffers from double vision. At the same time, however, depth perception is lost. And, if the same eye is always turned in, the eye can become so ignored that it goes partially blind. This partial blindness is called “amblyopia.”
Causes of Strabismus
Strabismus is typically a brain problem, not an eye muscle problem. Each eye has six muscles that control eye movement, but in most cases of strabismus, these muscles are normal. The issue arises when the brain fails to coordinate these muscles to align the eyes correctly. Factors like genetics, poor vision in one eye, or medical conditions can contribute to the development of strabismus.
Treatments for Strabismus
Non-Surgical Treatments
Many people wonder, “Can you fix strabismus without surgery? The answer is yes, you can fix strabismus without surgery several are available:
-
Vision Therapy
- Vision therapy for strabismus involves exercises that improve eye-brain coordination. This therapy can significantly help in aligning the eyes and enhancing depth perception. It is effective for both children and adults and is often used in combination with other treatments.
- Vision therapy works by providing biofeedback to teach the brain to blend the information from the two eyes (fusion). Eye alignment is then rewarded with 3D vision. Frequently this process can align eyes without surgery. In other cases, vision therapy is performed after surgery to help keep the eyes aligned and to improve depth perception for school, sports and driving.
-
Glasses for Strabismus
- Sometimes a patient is far-sighted so that the muscles inside the eye have to contract for clear seeing. As the brain contracts the muscles it also tells the eye to turn inward. This condition is called “accommodative esotropia”. In such cases, glasses will straighten the eye at least temporarily. In about half these cases, if nothing else is done, the eye will turn and surgery be recommended. In other cases, the far-sightedness will gradually disappear after age nine eliminating the need for glasses.
-
Eye Patching
- If the strabismus is unilateral (meaning that the same eye always turns in) the “good” eye may be patched to make the “bad” eye work and avoid vision loss. While such patching preserves sight, it does little to develop depth perception and can occasionally cause the strabismus to decompensate and the eye to turn in more often.
NON-SURGICAL CURE RATES
Studies show that 60–80% of patients achieve significant improvement in alignment with one surgery, though some may need additional surgery later. Success is generally higher in childhood-onset strabismus when surgery is performed early, but adults can also experience substantial improvement.
Surgical Treatments
- Eye Muscle Surgery
- This procedure alters the muscles around the eyes to improve alignment. The success rate of strabismus surgery varies, but it often requires post-operative vision therapy to maintain results. The cost of eye muscle surgery can vary widely based on the complexity of the case where you live.
- Eye muscle surgery is frequently cosmetic in nature. The strabismus surgery provides a false sense of security by making the eyes look straight to mask the fact that the information from the two eyes is still not being blended properly in the brain. Without this blending, there is nothing to maintain the eyes in proper alignment and additional surgeries may be needed.
- Types of Strabismus Surgery
- Eye muscle surgery for strabismus is typically performed under general anesthesia and involves different approaches depending on the type and severity of strabismus:
- Recession – Weakening an overactive eye muscle by moving it back on the eye. This reduces the muscle’s strength, helping to realign the eye.
- Resection -Strengthens a weak eye muscle by removing a small section, making it shorter and more effective at pulling the eye into the correct position.
- Adjustable Sutures – Some procedures may use adjustable sutures, allowing for fine-tuning of eye alignment shortly after surgery. This can be especially useful in adults where slight adjustments may improve outcomes.
How It Works
The goal of eye muscle surgery is to create a better balance between the eye muscles to improve alignment. Surgeons target specific muscles around one or both eyes, adjusting the length or placement of these muscles to alter the eye’s positioning.
After surgery, patients are often prescribed vision therapy, which includes exercises designed to help the brain and eyes work together for improved depth perception and eye coordination. Recovery from eye muscle surgery is usually brief, with most patients resuming normal activities within a few days. Some common post-surgical experiences include mild pain, redness, and temporary double vision. Full recovery and eye alignment may take a few weeks.
Risks
Possible side effects include double vision, infection, or, in rare cases, an under- or over-correction that may necessitate additional surgery.
Some patients may experience a temporary recurrence of misalignment, requiring additional interventions such as vision therapy.
Symptoms of Strabismus
Strabismus can present with various symptoms that may vary in severity. Recognizing these symptoms early can help in seeking timely treatment and avoiding further complications. Here are some common symptoms of strabismus:
- Misaligned Eyes: The most noticeable symptom is the misalignment of the eyes, where one eye may turn inwards (esotropia), outwards (exotropia), upwards (hypertropia), or downwards (hypotropia) .
- Double Vision: Individuals with strabismus may experience double vision (diplopia) because the brain receives two different images from the eyes that it cannot merge into a single image .
- Eye Strain: Frequent squinting or closing one eye to see better can indicate eye strain caused by strabismus .
- Difficulty with Depth Perception: Strabismus can impair depth perception, making it challenging to judge distances accurately. This can affect activities like driving, sports, and even simple tasks like pouring liquids .
- Head Tilting or Turning: Some individuals may tilt or turn their head to use their eyes together more effectively, which can be a compensatory behavior to reduce double vision .
- Frequent Blinking or Rubbing Eyes: Discomfort and eye fatigue can cause frequent blinking or rubbing of the eyes .
- Poor Eye Coordination: Difficulty in coordinating eye movements can result in an inability to track moving objects smoothly .
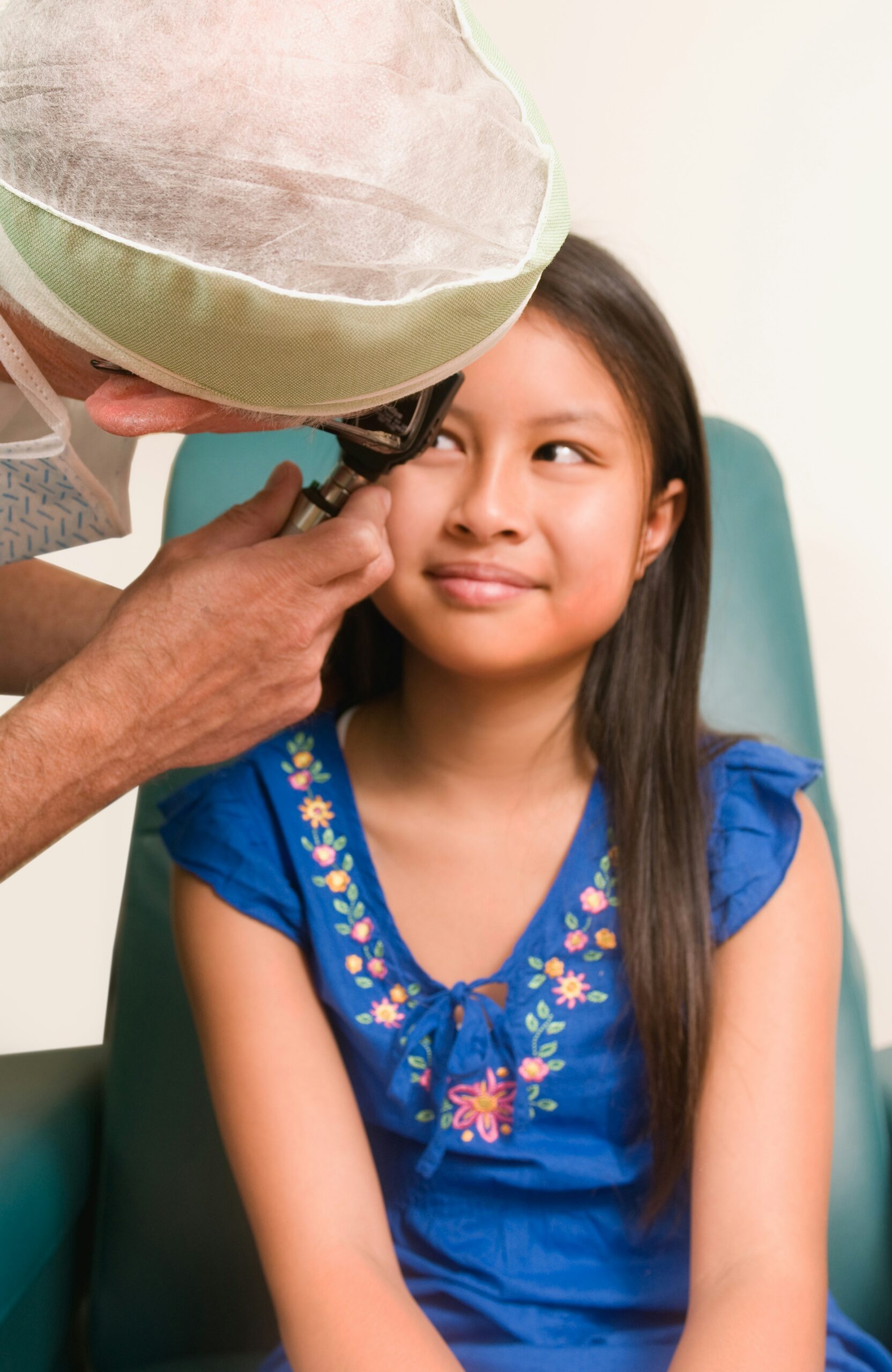

How Strabismus is Diagnosed
Diagnosing strabismus involves a comprehensive eye examination by an eye care professional, such as an optometrist or ophthalmologist. The following steps are typically involved in the diagnostic process:
- Medical History: The eye doctor will begin by taking a detailed medical history, including any symptoms experienced, family history of eye conditions, and any previous treatments or surgeries .
- Visual Acuity Test: This test measures the clarity of vision in each eye individually to determine if there is any vision impairment .
- Refraction Test: This test determines the appropriate lens prescription needed to correct refractive errors such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism, which can sometimes contribute to strabismus .
- Alignment and Focusing Tests: The doctor will assess how well the eyes align and focus together. This can involve cover tests, where one eye is covered while the other eye’s movement is observed, and other specialized tests to evaluate eye coordination and muscle function .
- Dilated Eye Exam: Dilating the pupils allows the doctor to examine the internal structures of the eye, including the retina, optic nerve, and blood vessels, to rule out any underlying conditions that may be contributing to strabismus .
- Binocular Vision Tests: These tests evaluate how well both eyes work together to form a single image. They help in assessing depth perception and the ability to maintain proper eye alignment .
- Corneal Light Reflex Test: This simple test involves shining a light into the eyes and observing the reflection on the corneas to check for symmetry in eye alignment .
- Prism Testing: Prisms may be used to measure the degree of misalignment by observing how light bends as it passes through the prism in front of the eyes .
Early diagnosis and treatment of strabismus are crucial to prevent complications such as amblyopia (lazy eye) and to improve overall visual function. If you or your child exhibit symptoms of strabismus, it is essential to schedule an eye examination with a qualified eye care professional .

Strabismus in Adults vs. Children
In children, early diagnosis and treatment are critical to prevent long-term vision problems such as amblyopia. In adults, the focus may shift towards managing symptoms and improving quality of life .
Causes: Childhood strabismus is often congenital or due to refractive errors, whereas adult strabismus can be caused by medical conditions, injuries, or residual childhood strabismus .
Symptoms: While both groups can experience misaligned eyes and vision issues, adults are more likely to report double vision and headaches .
Treatment Approaches: Children benefit greatly from early interventions like glasses, patching, and surgery, whereas adults may also use prism glasses and Botox in addition to traditional treatments .
Understanding these differences can help tailor the most effective treatment plans for individuals of all ages affected by strabismus.
Strabismus affects both how a child or adult looks and sees. Successful treatment aligns eyes and creates two-eyed depth perception for seeing the three-dimensional beauty of the world.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Is Strabismus Curable?
Strabismus can often be effectively treated and managed, especially when diagnosed early. Both non-surgical and surgical treatments can lead to significant improvements .
-
Can Glasses Fix Cross Eye?
-
How Long Does It Take to Correct Strabismus?
-
Can Adults Benefit from Strabismus Treatments?
-
What is Strabismus Vision Therapy?
-
Can Eye Exercises Fix Strabismus?
-
What are the Costs of Strabismus Treatments?
-
How Effective is Eye Patching for Strabismus?
-
Can Strabismus be Corrected in Adults?
-
What is the Success Rate of Strabismus Surgery?
-
Does Strabismus Affect Vision?
-
Are There Natural Ways to Fix Cross Eyes?
-
What causes strabismus in children?
-
How is strabismus diagnosed?
-
Can adults get strabismus treatment?
-
Will strabismus go away without treatment?
-
Why does strabismus affect depth perception?
-
Are there non-surgical strabismus treatments for adults?
Check Out Our Resources
Dr. Cook’s Publications:
- Authored books VISUAL FITNESS and WHEN YOUR CHILD STRUGGLES.
- Published articles in top optometric journals.
- His article “Eyesight, infinity and the human heart” was voted “Best Non-Technical Article” by the Association of Optometric Editors.





